Have you noticed your horse struggling with a stiff hind leg, lameness, or difficulty rising from a lying position? It’s time to delve into the crucial role of the horse’s hind leg extensor tendon and explore how it impacts your equine companion’s mobility and overall well-being.
Pain Points:
- Observing your horse’s reluctance to bend or extend its hind leg can be a cause for concern, hinting at discomfort or even pain.
- A horse exhibiting an abnormal gait, favoring one hind leg over the other, may indicate an underlying issue with the extensor tendon.
The horse’s hind leg extensor tendon, a vital component of the musculoskeletal system, plays a pivotal role in enabling powerful hind leg extension, propelling the horse forward with each stride. Furthermore, it facilitates the horse’s ability to rise from a lying position, a crucial movement for grazing, resting, and maneuvering in various terrains.
The horse hind leg extensor tendon is a critical structure that:
- Enables powerful hind leg extension, propelling the horse forward.
- Facilitates rising from a lying position, essential for grazing, resting, and maneuvering.
- Impacts the horse’s overall mobility and athletic performance.
Understanding the significance of the hind leg extensor tendon empowers horse owners and riders to be vigilant in monitoring their equine partners’ well-being and seeking timely veterinary intervention when necessary. Regular exercise, proper nutrition, and preventive care contribute to maintaining healthy tendons and ensuring the horse’s continued athleticism and enjoyment of life.
Understanding the Horse Hind Leg Extensor Tendon: Structure and Function
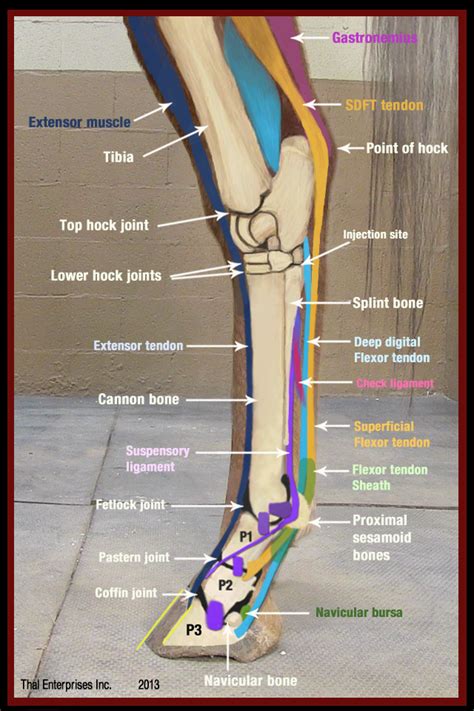
The horse hind leg extensor tendon, also known as the common calcaneal tendon, is a robust and critical structure that plays a pivotal role in the locomotion and overall performance of these majestic animals. This article delves into the anatomy, function, and potential injuries associated with this essential tendon.
Anatomy of the Horse Hind Leg Extensor Tendon
- Location: The horse hind leg extensor tendon is situated at the back of the lower hind leg, extending from the hock joint to the calcaneus (heel bone).
- Composition: This tendon is a thick, fibrous connective tissue primarily composed of collagen fibers arranged in parallel bundles.
- Attachments: Proximally, the tendon originates from the muscles of the hindquarters, including the biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus muscles. Distally, it inserts onto the calcaneus, acting as a powerful extensor of the hock joint.
Function of the Horse Hind Leg Extensor Tendon
- Extension of the Hock: The primary function of the extensor tendon is to extend the hock joint, enabling the horse to propel itself forward during locomotion.
- Energy Storage and Release: During movement, the tendon acts as a spring, storing elastic energy during the stance phase and releasing it during the propulsion phase, contributing to efficient movement.
- Shock Absorption: The tendon absorbs shock and impact forces generated during locomotion, protecting the joints and bones of the hind leg.
Injuries to the Horse Hind Leg Extensor Tendon
- Tendonitis: Inflammation of the extensor tendon is known as tendonitis. It can result from excessive strain, repetitive stress, or trauma.
- Tendon Strain: A strain is a partial tear of the tendon fibers, often caused by sudden forceful movements or overloading.
- Tendon Rupture: Complete tearing of the tendon is a severe injury that can occur due to extreme trauma or chronic degeneration.
Etiology of Horse Hind Leg Extensor Tendon Injuries
- Excessive Workload: Overtraining, long-distance races, or demanding jumping competitions can strain the tendon beyond its capacity.
- Improper Warm-Up: Insufficient warm-up before exercise can lead to muscle tightness and increased risk of tendon injuries.
- Hard Surfaces: Running or jumping on hard, unforgiving surfaces can impose excessive stress on the tendon.
- Uneven Footing: Uneven terrain or unstable footing can cause the horse to stumble or slip, potentially causing tendon injuries.
- Conformation Issues: Horses with certain conformational abnormalities, such as sickle hocks or cow hocks, may experience increased stress on the extensor tendon.
Diagnosis of Horse Hind Leg Extensor Tendon Injuries

- Physical Examination: Veterinarians perform a thorough physical examination, assessing the horse’s gait, palpating the tendon, and testing its flexibility.
- Ultrasound Imaging: Ultrasound provides real-time visualization of the tendon, allowing veterinarians to assess its integrity, detect tears or inflammation, and monitor healing progress.
- Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI): MRI offers detailed cross-sectional images of the tendon, enabling veterinarians to evaluate the extent and severity of injuries.
Treatment of Horse Hind Leg Extensor Tendon Injuries
- Rest and Immobilization: Initial treatment involves rest and immobilization of the affected leg to allow the tendon to heal.
- Anti-Inflammatory Medications: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSA