Have You Ever Wondered About the Complex Network of Muscles and Tendons in Your Legs? Here’s a Comprehensive Guide to Their Anatomy and Functions
Your legs are a fascinating biomechanical masterpiece, allowing you to perform various movements with ease. At the core of this intricate system lie the muscles and tendons, which work in harmony to generate power, stability, and flexibility. Understanding the anatomy of these structures is crucial for maintaining leg health and preventing injuries.
The leg muscle tendon diagram depicts the intricate network of muscles, tendons, and their attachments to bones. It serves as a roadmap to visualize the complex interactions between these structures and their role in various leg movements. This diagram is an invaluable resource for medical professionals, fitness enthusiasts, and anyone seeking a deeper understanding of their body’s mechanics.
By studying the leg muscle tendon diagram, one can gain insights into the coordination and precision with which muscles contract to produce movement. It also highlights the importance of maintaining flexibility in tendons to prevent strain or tears. This understanding empowers individuals to engage in targeted exercises and stretches to enhance their leg strength, mobility, and overall well-being.
In essence, the leg muscle tendon diagram is a gateway to comprehending the intricate workings of our lower extremities. Whether you’re a medical professional, an athlete, or simply curious about human anatomy, this diagram offers valuable insights into the fascinating world of muscles, tendons, and their vital role in our everyday movements.
Leg Muscle Tendon Diagram: An Anatomical Overview
Introducing the Leg Muscles and Tendons
The intricate interplay of muscles and tendons in the leg region plays a pivotal role in enabling movement, stability, and strength. To fully grasp the functionality of the leg, it is essential to comprehend the detailed anatomy of these structures. In this comprehensive guide, we will embark on a journey to explore the leg muscle tendon diagram, shedding light on their complex interactions.
Understanding the Quadriceps Group: The Powerhouse of Extension
- Vastus Lateralis: Behold the vastus lateralis, a robust muscle situated on the lateral aspect of the thigh. Its primary function is to extend the knee joint, propelling the leg forward during activities such as walking, running, and jumping.
- Vastus Medialis: Meet the vastus medialis, a muscle positioned on the medial side of the thigh. Working in tandem with the vastus lateralis, it plays a crucial role in extending the knee and maintaining stability during various movements.
- Vastus Intermedius: Allow us to introduce the vastus intermedius, a muscle located deep to the vastus lateralis and vastus medialis. It contributes to knee extension and aids in stabilizing the patella, preventing dislocation.
- Rectus Femoris: The rectus femoris, a unique muscle with a dual function, deserves special mention. Extending both the knee and the hip joint, this muscle plays a vital role in activities that demand both movements, such as climbing stairs or kicking a ball.
- Common Tendon of the Quadriceps: These four muscles, the vastus lateralis, vastus medialis, vastus intermedius, and rectus femoris, unite their forces to form a common tendon, a robust and resilient structure that attaches them to the patella, the kneecap.
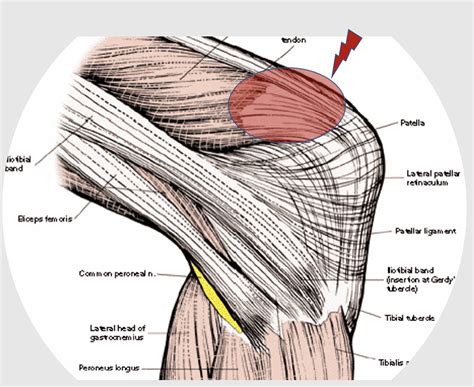
Exploring the Hamstring Group: Flexion and Stability
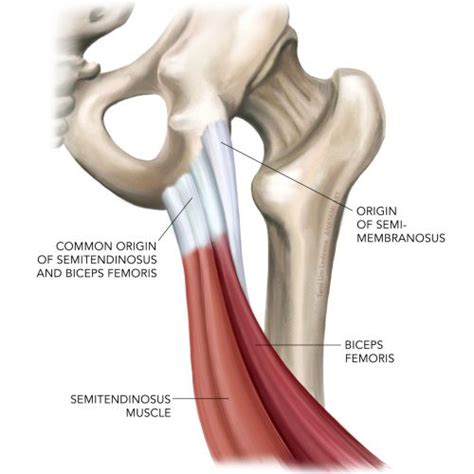
- Biceps Femoris: The biceps femoris, a two-headed muscle with its origin in the ischial tuberosity of the pelvis, takes center stage in the hamstring group. It flexes the knee joint and externally rotates the tibia, contributing to stability during movements like walking and running.
- Semitendinosus: Let us meet the semitendinosus, a slender muscle that originates from the ischial tuberosity and inserts onto the medial tibia. It assists in knee flexion and medial rotation of the tibia, contributing to overall leg stability.
- Semimembranosus: Introducing the semimembranosus, the most medial muscle of the hamstring group. This muscle arises from the ischial tuberosity and attaches to the posterior aspect of the medial tibial condyle. It aids in knee flexion and is involved in the stabilization of the knee joint.
- Common Tendon of the Hamstrings: These three muscles, the biceps femoris, semitendinosus, and semimembranosus, converge to form a robust common tendon that inserts onto the medial and lateral aspects of the proximal tibia.
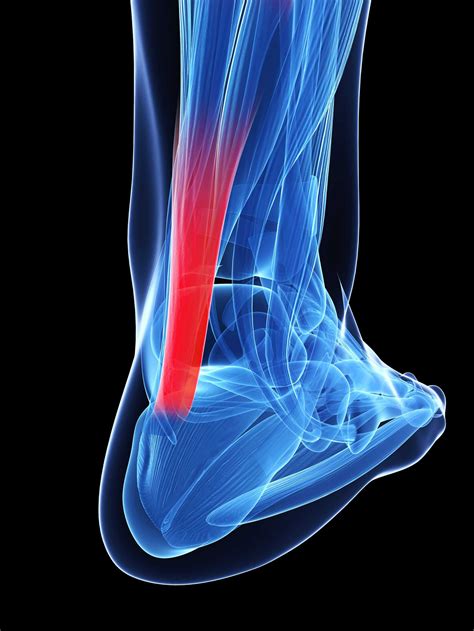
Unraveling the Calf Muscles: Propulsion and Support
- Gastrocnemius: Allow us to introduce the gastrocnemius, a powerful two-headed muscle that forms the bulk of the calf region. Arising from the condyles of the femur and inserting onto the calcaneus via the Achilles tendon, it is responsible for plantar flexion of the foot and propelling the body forward during activities like walking, running, and jumping.
- Soleus: Next, we have the soleus, a broad and flat muscle located deep to the gastrocnemius. It originates from the tibia and fibula and also inserts onto the calcaneus via the Achilles tendon. Working in concert with the gastrocnemius, the soleus aids in plantar flexion and contributes to maintaining stability during standing and walking.
- Achilles Tendon: The Achilles tendon, the strongest tendon in the human body, deserves special attention. Composed of a merger between the gastrocnemius and soleus tendons, it is a crucial structure that transmits the force generated by these muscles to the heel bone, enabling powerful movements like walking, running, and jumping.
A Symphony of Muscles and Tendons
In conclusion, the leg muscle tendon diagram showcases an intricate interplay of muscles and tendons, each contributing to the overall functionality of the leg. From the powerful quadriceps group responsible for extension to the flexible hamstrings involved in flexion and stability, and the robust calf muscles driving propulsion through plantar flexion, these structures work in unison to facilitate movement, support, and strength in the leg region. Understanding their intricate anatomy provides a deeper appreciation for the marvel of the human body.